MAJOR LANDFORMS OF THE EARTH- Class 6- Geography Chapter 6
- The surface of the earth is not the same everywhere. It has an infinite variety of landforms.
- Landforms are a result of two processes:
- Internal Process: The earth moves slowly. Within the earth, a continuous movement is taking place. The internal process leads to the upliftment and sinking of the earth’s surface at several places.
- External Process: It is the continuous wearing down (erosion) and rebuilding (deposition) of the earth’s surface. These activities are carried out by running water, ice and wind.
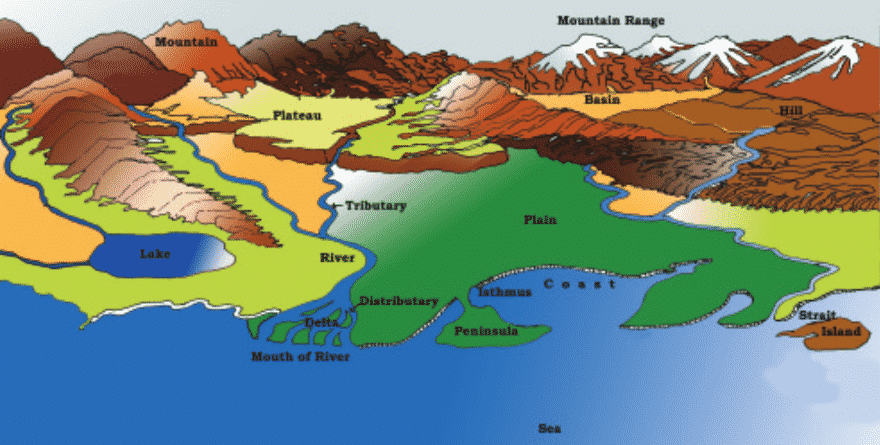
- Broadly, landforms can be grouped into mountains, plateaus and plains depending upon their elevation and slope.
Mountains
- It is any natural elevation of the earth surface. As you go higher, the climate becomes colder, which is the reason why less people live in mountain areas.
- In some mountains, there are permanently frozen rivers of ice called glaciers.
- Since the slopes are steep, less land is available for farming.
- Some mountains are under the sea. Mauna Kea (Hawaii) in the Pacific Ocean is an example. It is higher than Mt. Everest.
- Mountains may be arranged in a line known as range. For example, the Himalayas in Asia, the Alps in Europe and the Andes in South America.
- They are storehouses of water. Many rivers have their source in the glaciers in the mountains.
- The river valleys and terraces are ideal for cultivation of crops.
- Mountains have a rich variety of flora and fauna.
- There are three types of mountains:
- Fold Mountains: The Himalayan Mountains and the Alps are young fold mountains with rugged relief and high conical peaks.
- The Aravali range in India is one of the oldest fold mountain systems in the world. It has considerably worn down due to the processes of erosion.
- The Appalachians in North America and the Ural mountains in Russia have rounded features and low elevation. They are very old fold mountains.
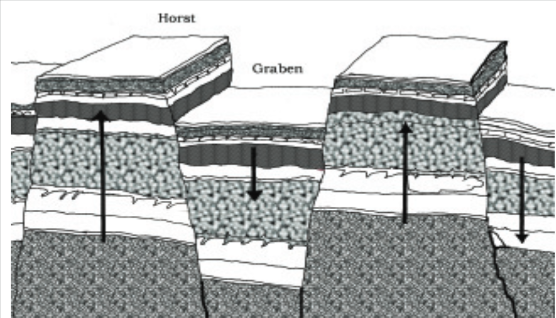
2. Block Mountains: They are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically.
- The uplifted blocks are termed as horsts.
- The lowered blocks are called graben.
- Example: the Rhine valley and the Vosges mountain in Europe.
3. Volcanic Mountains: They are formed due to volcanic activity.
- Example: Mt. Kilimanjaro in Kenya, Africa and Mt. Fujiyama in Japan.
Plateaus
- It is an elevated flat land.
- It is a flat-topped table land standing above the surrounding area.
- It may have one or more sides with steep slopes.
- The height varies from few hundred metres to several thousand metres.
- They are also young and old, like the mountains.
- The Deccan plateau in India is one of the oldest plateaus.
- The Tibet plateau is the highest plateau in the world.
- They are rich in mineral deposits. Hence, many of the mining areas in the world are located in the plateau areas.
- African plateau is famous for gold and diamond mining.
- In India, huge reserves of iron, coal and manganese are found in the Chhotanagpur plateau.
- In the plateau areas, there may be several waterfalls as the river falls from a great height. For example : Hundru falls in the Chhotanagpur plateau and the Jog falls in Karnataka.
- The lava plateaus are rich in black soil that are fertile and good for cultivation.
Plains
- They are large stretches of flat land.
- They are not more than 200 metres above mean sea level.
- Most of them are formed by rivers and their tributaries.
- The rivers flow down the slopes of mountains and erode them.
- They carry forward the eroded material. Then they deposit their load consisting of stones, sand and silt along their courses and in their valleys. It is from these deposits that plains are formed.
- Generally, plains are very fertile, because of which the land is highly productive for cultivation.
- Construction of transport network is easy. Thus, they are the most thickly populated regions of the world.
- In India too, the Indo-Gangetic plains are the most densely populated regions of the country.
Read More: MAJOR DOMAINS OF THE EARTH- Class 6- Geography Chapter 5