The Mauryan Empire
- The Mauryan Empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya more than 2300 years ago.
- When members of the same family become rulers one after another, it is called a dynasty.
- The Mauryas were a dynasty with three important rulers- Chandragupta, his son Bindusara who was the father of Ashoka.
- Chandragupta was supported by a wise man named Chanakya or Kautilya, many of whose ideas were written down in a book called the Arthashastra.
Read More: Class 6 Ch 7 History
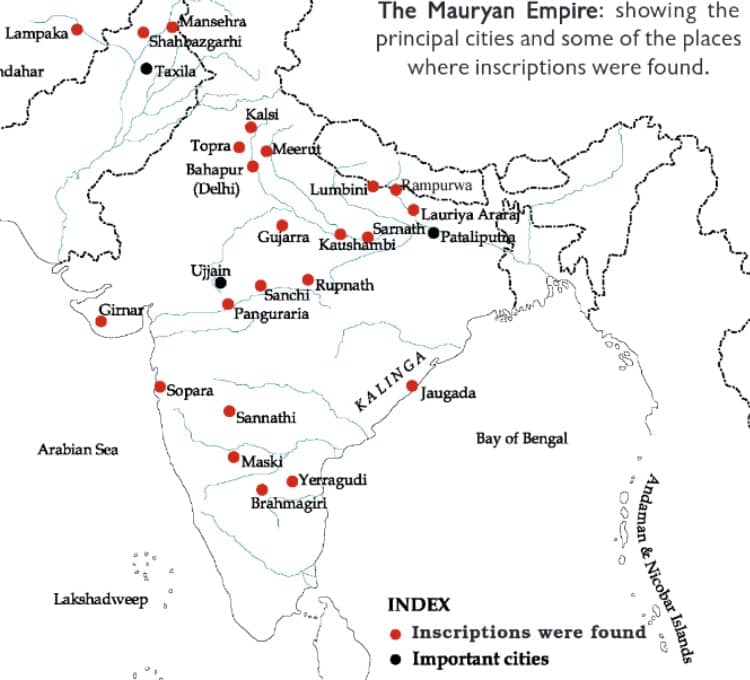
Important cities in the empire
- Capital Pataliputra
- Taxila- it was a gateway to the north-west, including Central Asia.
- Ujjain- it lay on the route from north to south India.
- Merchants, officials and crafts persons probably lived in these cities.
Empires v/s Kingdoms
- Emperors need more resources than kings because empires are larger than kingdoms, and need to be protected by big armies.
- They also need a large number of officials to collect taxes.
Ruling the Empire
- The empire was very large.
- The area around Pataliputra was under the direct control of the emperor.
- Officials collected taxes from the area under the direct control of the ruler.
- Royal princes often went to the provinces as governors.
- The Mauryan rulers tried to control roads and rivers which were important for transport.
- People in forested regions provided the Mauryan officials with elephants, timber, honey and wax.
- Taxes and tributes were collected.
- Unlike taxes, which were collected on a regular basis, tribute was collected as and when it was possible from people who gave a variety of things, more or less willingly.
- Megasthenes was an ambassador who was sent to the court of Chandragupta Maurya by the Greek ruler of West Asia named Seleucus Nicator.
Ashoka
- He was the most famous of the Mauryan rulers.
- He was the first ruler who tried to take his message to the people through inscriptions.
- Most of his inscriptions were in Prakrit and were written in the Brahmi script.
- He fought a war to conquer Kalinga (ancient name of coastal Odisha).
- Horrified by the violence and bloodshed, he decided not to fight any more wars.
- He is the only king in the history of the world who gave up conquest after winning a war.
Ashoka’s Dhamma
- He was inspired by the teachings of Buddha.
- His dhamma did not involve worshiping of a God or performing a sacrifice.
- He appointed officials known as Dhamma mahamatta, who went from place to place teaching people about dhamma.
- Problems in his empire like religious conflicts, animal sacrifices, ill treatment of slaves and servants and family quarrels troubled Ashoka, who felt it was his duty to solve them.
- On Ashoka’s instructions, inscriptions were carved on pillars and on rock surfaces.
- He also sent messengers to spread ideas about dhamma to countries like Syria, Egypt, Greece and Sri Lanka.
- He built roads, dug wells and rest houses.
- He arranged for medical treatment for both human beings and animals.
- The Lion Capital was carved in stone, and placed on top of a massive stone pillar at Sarnath.

- The Rampurva bull is a finely polished stone sculpture.

- It was part of a Mauryan pillar, found in Rampurva, Bihar and is now placed in the Rashtrapati Bhavan.










Nice it is very helpful